12. L3 Forwarding with Access Control Sample Application¶
The L3 Forwarding with Access Control application is a simple example of packet processing using the DPDK. The application performs a security check on received packets. Packets that are in the Access Control List (ACL), which is loaded during initialization, are dropped. Others are forwarded to the correct port.
12.1. Overview¶
The application demonstrates the use of the ACL library in the DPDK to implement access control and packet L3 forwarding. The application loads two types of rules at initialization:
- Route information rules, which are used for L3 forwarding
- Access Control List (ACL) rules that blacklist (or block) packets with a specific characteristic
When packets are received from a port, the application extracts the necessary information from the TCP/IP header of the received packet and performs a lookup in the rule database to figure out whether the packets should be dropped (in the ACL range) or forwarded to desired ports. The initialization and run-time paths are similar to those of the L3 forwarding application (see Chapter 10, “L3 Forwarding Sample Application” for more information). However, there are significant differences in the two applications. For example, the original L3 forwarding application uses either LPM or an exact match algorithm to perform forwarding port lookup, while this application uses the ACL library to perform both ACL and route entry lookup. The following sections provide more detail.
Classification for both IPv4 and IPv6 packets is supported in this application. The application also assumes that all the packets it processes are TCP/UDP packets and always extracts source/destination port information from the packets.
12.1.1. Tuple Packet Syntax¶
The application implements packet classification for the IPv4/IPv6 5-tuple syntax specifically. The 5-tuple syntax consist of a source IP address, a destination IP address, a source port, a destination port and a protocol identifier. The fields in the 5-tuple syntax have the following formats:
- Source IP address and destination IP address : Each is either a 32-bit field (for IPv4), or a set of 4 32-bit fields (for IPv6) represented by a value and a mask length. For example, an IPv4 range of 192.168.1.0 to 192.168.1.255 could be represented by a value = [192, 168, 1, 0] and a mask length = 24.
- Source port and destination port : Each is a 16-bit field, represented by a lower start and a higher end. For example, a range of ports 0 to 8192 could be represented by lower = 0 and higher = 8192.
- Protocol identifier : An 8-bit field, represented by a value and a mask, that covers a range of values. To verify that a value is in the range, use the following expression: “(VAL & mask) == value”
The trick in how to represent a range with a mask and value is as follows. A range can be enumerated in binary numbers with some bits that are never changed and some bits that are dynamically changed. Set those bits that dynamically changed in mask and value with 0. Set those bits that never changed in the mask with 1, in value with number expected. For example, a range of 6 to 7 is enumerated as 0b110 and 0b111. Bit 1-7 are bits never changed and bit 0 is the bit dynamically changed. Therefore, set bit 0 in mask and value with 0, set bits 1-7 in mask with 1, and bits 1-7 in value with number 0b11. So, mask is 0xfe, value is 0x6.
Note
The library assumes that each field in the rule is in LSB or Little Endian order when creating the database. It internally converts them to MSB or Big Endian order. When performing a lookup, the library assumes the input is in MSB or Big Endian order.
12.1.2. Access Rule Syntax¶
In this sample application, each rule is a combination of the following:
- 5-tuple field: This field has a format described in Section.
- priority field: A weight to measure the priority of the rules. The rule with the higher priority will ALWAYS be returned if the specific input has multiple matches in the rule database. Rules with lower priority will NEVER be returned in any cases.
- userdata field: A user-defined field that could be any value. It can be the forwarding port number if the rule is a route table entry or it can be a pointer to a mapping address if the rule is used for address mapping in the NAT application. The key point is that it is a useful reserved field for user convenience.
12.1.3. ACL and Route Rules¶
The application needs to acquire ACL and route rules before it runs. Route rules are mandatory, while ACL rules are optional. To simplify the complexity of the priority field for each rule, all ACL and route entries are assumed to be in the same file. To read data from the specified file successfully, the application assumes the following:
- Each rule occupies a single line.
- Only the following four rule line types are valid in this application:
- ACL rule line, which starts with a leading character ‘@’
- Route rule line, which starts with a leading character ‘R’
- Comment line, which starts with a leading character ‘#’
- Empty line, which consists of a space, form-feed (‘f’), newline (‘n’), carriage return (‘r’), horizontal tab (‘t’), or vertical tab (‘v’).
Other lines types are considered invalid.
- Rules are organized in descending order of priority, which means rules at the head of the file always have a higher priority than those further down in the file.
- A typical IPv4 ACL rule line should have a format as shown below:
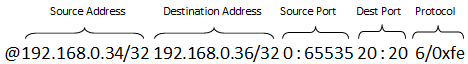
IPv4 addresses are specified in CIDR format as specified in RFC 4632. They consist of the dot notation for the address and a prefix length separated by ‘/’. For example, 192.168.0.34/32, where the address is 192.168.0.34 and the prefix length is 32.
Ports are specified as a range of 16-bit numbers in the format MIN:MAX, where MIN and MAX are the inclusive minimum and maximum values of the range. The range 0:65535 represents all possible ports in a range. When MIN and MAX are the same value, a single port is represented, for example, 20:20.
The protocol identifier is an 8-bit value and a mask separated by ‘/’. For example: 6/0xfe matches protocol values 6 and 7.
- Route rules start with a leading character ‘R’ and have the same format as ACL rules except an extra field at the tail that indicates the forwarding port number.
12.1.4. Rules File Example¶
Figure 5 is an example of a rules file. This file has three rules, one for ACL and two for route information.
Figure 5.Example Rules File
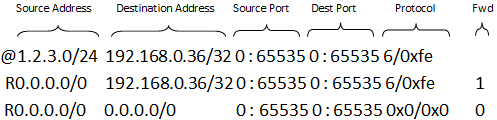
Each rule is explained as follows:
- Rule 1 (the first line) tells the application to drop those packets with source IP address = [1.2.3.*], destination IP address = [192.168.0.36], protocol = [6]/[7]
- Rule 2 (the second line) is similar to Rule 1, except the source IP address is ignored. It tells the application to forward packets with destination IP address = [192.168.0.36], protocol = [6]/[7], destined to port 1.
- Rule 3 (the third line) tells the application to forward all packets to port 0. This is something like a default route entry.
As described earlier, the application assume rules are listed in descending order of priority, therefore Rule 1 has the highest priority, then Rule 2, and finally, Rule 3 has the lowest priority.
Consider the arrival of the following three packets:
- Packet 1 has source IP address = [1.2.3.4], destination IP address = [192.168.0.36], and protocol = [6]
- Packet 2 has source IP address = [1.2.4.4], destination IP address = [192.168.0.36], and protocol = [6]
- Packet 3 has source IP address = [1.2.3.4], destination IP address = [192.168.0.36], and protocol = [8]
Observe that:
- Packet 1 matches all of the rules
- Packet 2 matches Rule 2 and Rule 3
- Packet 3 only matches Rule 3
For priority reasons, Packet 1 matches Rule 1 and is dropped. Packet 2 matches Rule 2 and is forwarded to port 1. Packet 3 matches Rule 3 and is forwarded to port 0.
For more details on the rule file format, please refer to rule_ipv4.db and rule_ipv6.db files (inside <RTE_SDK>/examples/l3fwd-acl/).
12.1.5. Application Phases¶
Once the application starts, it transitions through three phases:
Initialization Phase - Perform the following tasks:
Parse command parameters. Check the validity of rule file(s) name(s), number of logical cores, receive and transmit queues. Bind ports, queues and logical cores. Check ACL search options, and so on.
Call Environmental Abstraction Layer (EAL) and Poll Mode Driver (PMD) functions to initialize the environment and detect possible NICs. The EAL creates several threads and sets affinity to a specific hardware thread CPU based on the configuration specified by the command line arguments.
Read the rule files and format the rules into the representation that the ACL library can recognize. Call the ACL library function to add the rules into the database and compile them as a trie of pattern sets. Note that application maintains a separate AC contexts for IPv4 and IPv6 rules.
Runtime Phase - Process the incoming packets from a port. Packets are processed in three steps:
- Retrieval: Gets a packet from the receive queue. Each logical core may process several queues for different ports. This depends on the configuration specified by command line arguments.
- Lookup: Checks that the packet type is supported (IPv4/IPv6) and performs a 5-tuple lookup over corresponding AC context. If an ACL rule is matched, the packets will be dropped and return back to step 1. If a route rule is matched, it indicates the packet is not in the ACL list and should be forwarded. If there is no matches for the packet, then the packet is dropped.
- Forwarding: Forwards the packet to the corresponding port.
Final Phase - Perform the following tasks:
Calls the EAL, PMD driver and ACL library to free resource, then quits.
12.2. Compiling the Application¶
To compile the application:
Go to the sample application directory:
export RTE_SDK=/path/to/rte_sdk cd ${RTE_SDK}/examples/l3fwd-acl
Set the target (a default target is used if not specified). For example:
export RTE_TARGET=x86_64-native-linuxapp-gccSee the DPDK IPL Getting Started Guide for possible RTE_TARGET values.
Build the application:
make
12.3. Running the Application¶
The application has a number of command line options:
./build/l3fwd-acl [EAL options] -- -p PORTMASK [-P] --config(port,queue,lcore)[,(port,queue,lcore)] --rule_ipv4 FILENAME rule_ipv6 FILENAME [--scalar] [--enable-jumbo [--max-pkt-len PKTLEN]] [--no-numa]
where,
- -p PORTMASK: Hexadecimal bitmask of ports to configure
- -P: Sets all ports to promiscuous mode so that packets are accepted regardless of the packet’s Ethernet MAC destination address. Without this option, only packets with the Ethernet MAC destination address set to the Ethernet address of the port are accepted.
- –config (port,queue,lcore)[,(port,queue,lcore)]: determines which queues from which ports are mapped to which cores
- –rule_ipv4 FILENAME: Specifies the IPv4 ACL and route rules file
- –rule_ipv6 FILENAME: Specifies the IPv6 ACL and route rules file
- –scalar: Use a scalar function to perform rule lookup
- –enable-jumbo: optional, enables jumbo frames
- –max-pkt-len: optional, maximum packet length in decimal (64-9600)
- –no-numa: optional, disables numa awareness
As an example, consider a dual processor socket platform where cores 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 appear on socket 0, while cores 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 11 appear on socket 1. Let’s say that the user wants to use memory from both NUMA nodes, the platform has only two ports and the user wants to use two cores from each processor socket to do the packet processing.
To enable L3 forwarding between two ports, using two cores from each processor, while also taking advantage of local memory access by optimizing around NUMA, the user must enable two queues from each port, pin to the appropriate cores and allocate memory from the appropriate NUMA node. This is achieved using the following command:
./build/l3fwd-acl -c f -n 4 -- -p 0x3 --config="(0,0,0),(0,1,2),(1,0,1),(1,1,3)" --rule_ipv4="./rule_ipv4.db" -- rule_ipv6="./rule_ipv6.db" --scalar
In this command:
The -c option enables cores 0, 1, 2, 3
The -p option enables ports 0 and 1
The –config option enables two queues on each port and maps each (port,queue) pair to a specific core. Logic to enable multiple RX queues using RSS and to allocate memory from the correct NUMA nodes is included in the application and is done transparently. The following table shows the mapping in this example:
Port
Queue
lcore
Description
0
0
0
Map queue 0 from port 0 to lcore 0.
0
1
2
Map queue 1 from port 0 to lcore 2.
1
0
1
Map queue 0 from port 1 to lcore 1.
1
1
3
Map queue 1 from port 1 to lcore 3.
The –rule_ipv4 option specifies the reading of IPv4 rules sets from the ./ rule_ipv4.db file.
The –rule_ipv6 option specifies the reading of IPv6 rules sets from the ./ rule_ipv6.db file.
The –scalar option specifies the performing of rule lookup with a scalar function.
12.4. Explanation¶
The following sections provide some explanation of the sample application code. The aspects of port, device and CPU configuration are similar to those of the L3 forwarding application (see Chapter 10, “L3 Forwarding Sample Application” for more information). The following sections describe aspects that are specific to L3 forwarding with access control.
12.4.1. Parse Rules from File¶
As described earlier, both ACL and route rules are assumed to be saved in the same file. The application parses the rules from the file and adds them to the database by calling the ACL library function. It ignores empty and comment lines, and parses and validates the rules it reads. If errors are detected, the application exits with messages to identify the errors encountered.
The application needs to consider the userdata and priority fields. The ACL rules save the index to the specific rules in the userdata field, while route rules save the forwarding port number. In order to differentiate the two types of rules, ACL rules add a signature in the userdata field. As for the priority field, the application assumes rules are organized in descending order of priority. Therefore, the code only decreases the priority number with each rule it parses.
12.4.2. Setting Up the ACL Context¶
For each supported AC rule format (IPv4 5-tuple, IPv6 6-tuple) application creates a separate context handler from the ACL library for each CPU socket on the board and adds parsed rules into that context.
Note, that for each supported rule type, application needs to calculate the expected offset of the fields from the start of the packet. That’s why only packets with fixed IPv4/ IPv6 header are supported. That allows to perform ACL classify straight over incoming packet buffer - no extra protocol field retrieval need to be performed.
Subsequently, the application checks whether NUMA is enabled. If it is, the application records the socket IDs of the CPU cores involved in the task.
Finally, the application creates contexts handler from the ACL library, adds rules parsed from the file into the database and build an ACL trie. It is important to note that the application creates an independent copy of each database for each socket CPU involved in the task to reduce the time for remote memory access.